The practical provided the opportunity to put both basic deep learning ideas into practice, and explore the slightly more advanced topic of Convolutional Neural Networks on MNIST, CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets.
For tasks 1 and 2, the basic neural network components written in Python were provided, but often with the more advanced implementations left for us to fill in, e.g. modifications to the optimizer to support learning rate decay. Here, we only used MNIST.
In tasks 3 and 4 we used TensorFlow and both Densely connected neural networks, and Convolutional Neural Networks to classify images in CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets.
- Task 1: Establish a baseline for MNIST classification using densely connected neural networks and investigating different learning rate schedules.
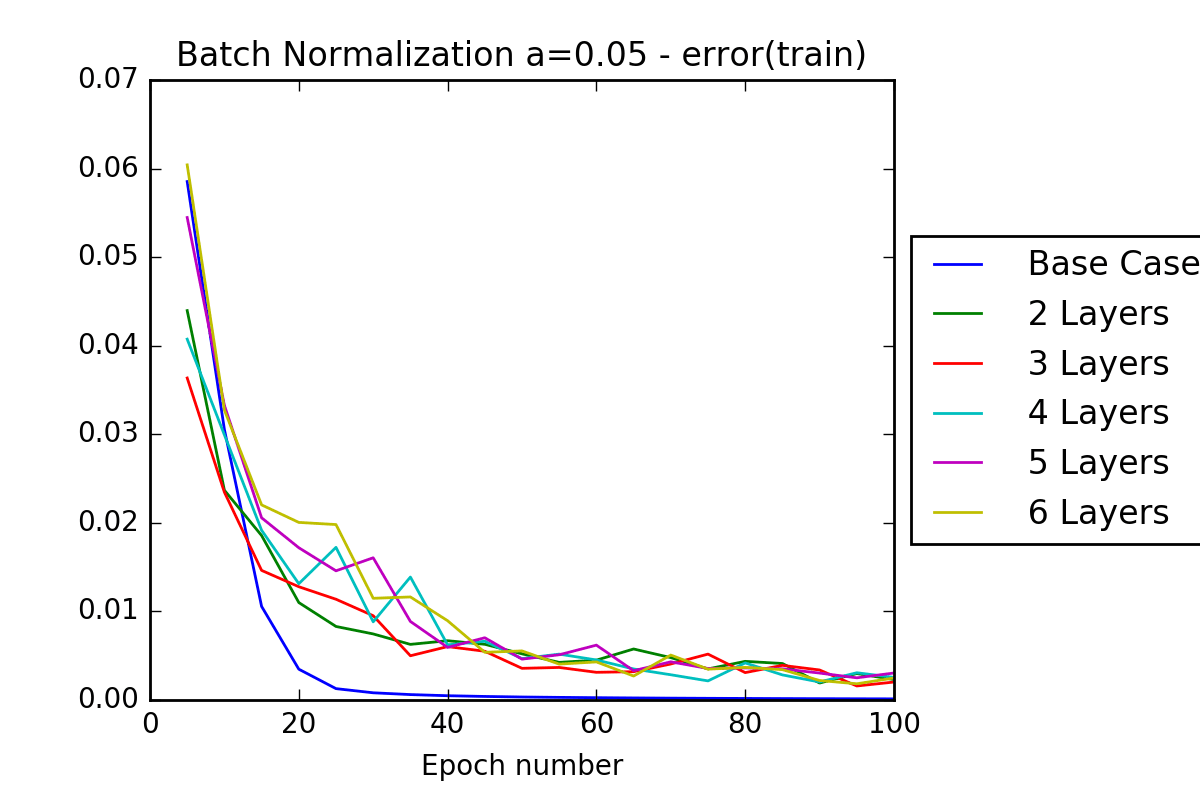
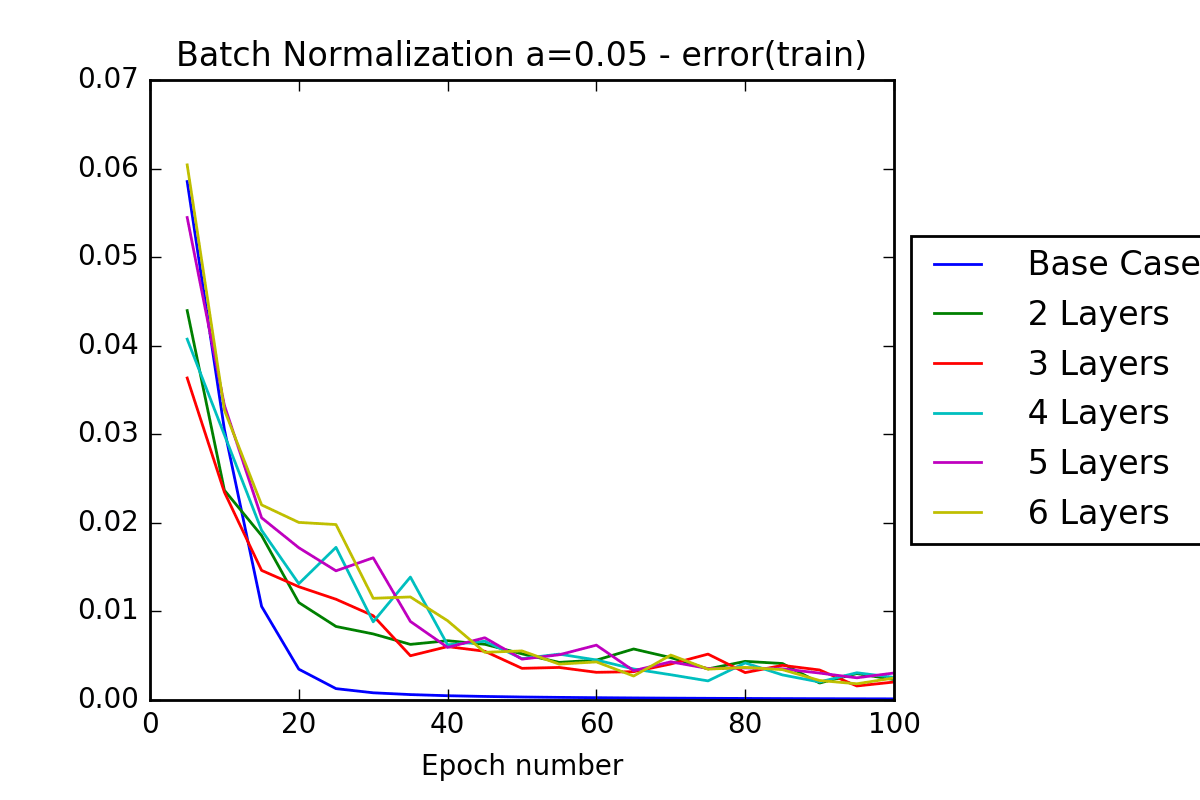
- Task 2: Experiment with different network configurations, observing how much different layer count, hyperparameter tuning and batch normalization can increase the classification accuracy above the baseline. Data augmentation was used due to limited datasets and provided good results.
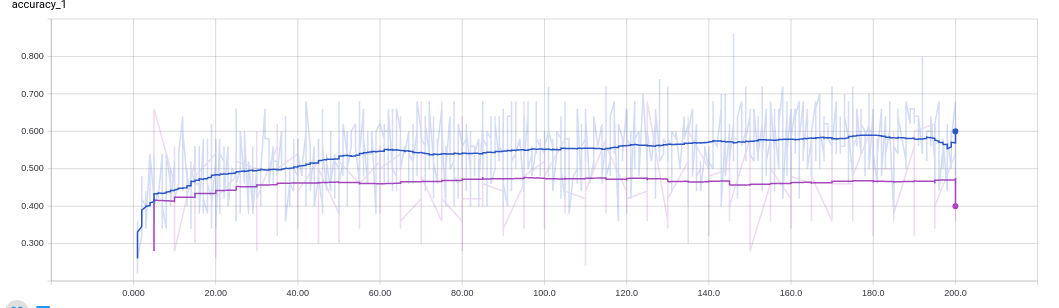
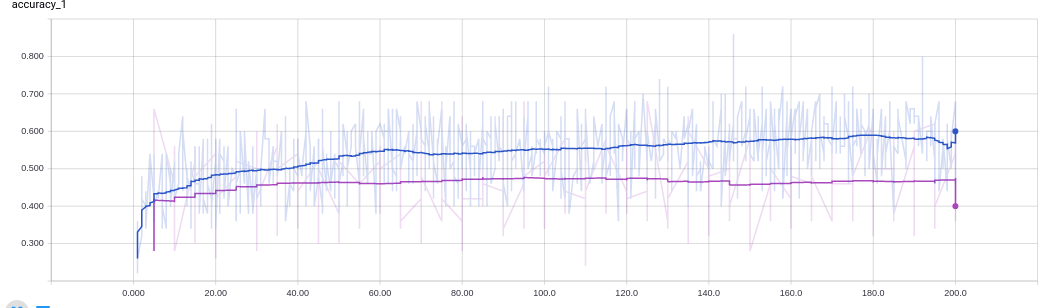
- Task 3: Perform experiments to determine the baseline accuracy that a densely connected neural network can achieve. I have experimented with different numbers of hidden units, epochs, activation functions, adaptive learning rate variations and dropout.
- Task 4: Investigate the use of Convolutional neural networks for image recognition in CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets. Here I have experimented with CNNs, different network configurations, hyperparameters, as well as dropout, fractional max-pooling and data augmentation.
Reports: Google Drive
Code Repository: GitLab